The brain is a complex organ. So, brain injuries can produce many long-term effects which vary greatly from one patient to the next. This can make it difficult specify equipment to help brain injury patients. Something that works well for one person won’t necessarily work for someone else who has a different type of brain injury that produces different symptoms.
A brain injury can affect someone cognitively, behaviourally and physically. Specialist seating can provide support in all these areas, which makes finding the correct chair key when caring for someone with a brain injury.
This simple guide will help you to choose the right chair for individual brain injury patients.
Jump straight to…
What is a brain injury?
The term brain injury covers all injuries to the brain that occur after birth — sometimes called acquired brain injury (ABI). It does not typically include neurological disorders that result from brain injury or brain malformation during pregnancy, such as Cerebral Palsy.
Common causes of brain injury are:
- Strokes
- Brain Tumours
- Encephalitis (inflammation of the brain)
- Traumatic head injury (from a fall, traffic accident etc.)
Brain injuries caused by traumatic head injury fall under their own category called traumatic brain injury (TBI).
When specifying care equipment, particularly specialist seating, the symptoms of a brain injury are often more important than the cause. The severity and location of the brain injury will determine the symptoms someone shows.
Best Chairs for Brain Injury Rehabilitation
The complexity of the brain also gives it an incredible ability to heal. Over time and with specialist rehabilitation, a healthy area of the brain can often start to compensate for the injured part of the brain.
This is important when choosing a chair for a brain injury patient. You want a chair that is flexible enough to support them through their entire recovery process.
Here are some key features to look out for when selecting seating for rehabilitation:
Adjustable levels of support
By opting for a chair that offers adjustable levels of support, you avoid having to replace the chair as the patient’s condition improves.
This reduces the time and cost associated with supplying multiple chairs. More importantly, it allows the user to focus on their rehabilitation rather than repeatedly having their routine disrupted by getting used to new chairs.
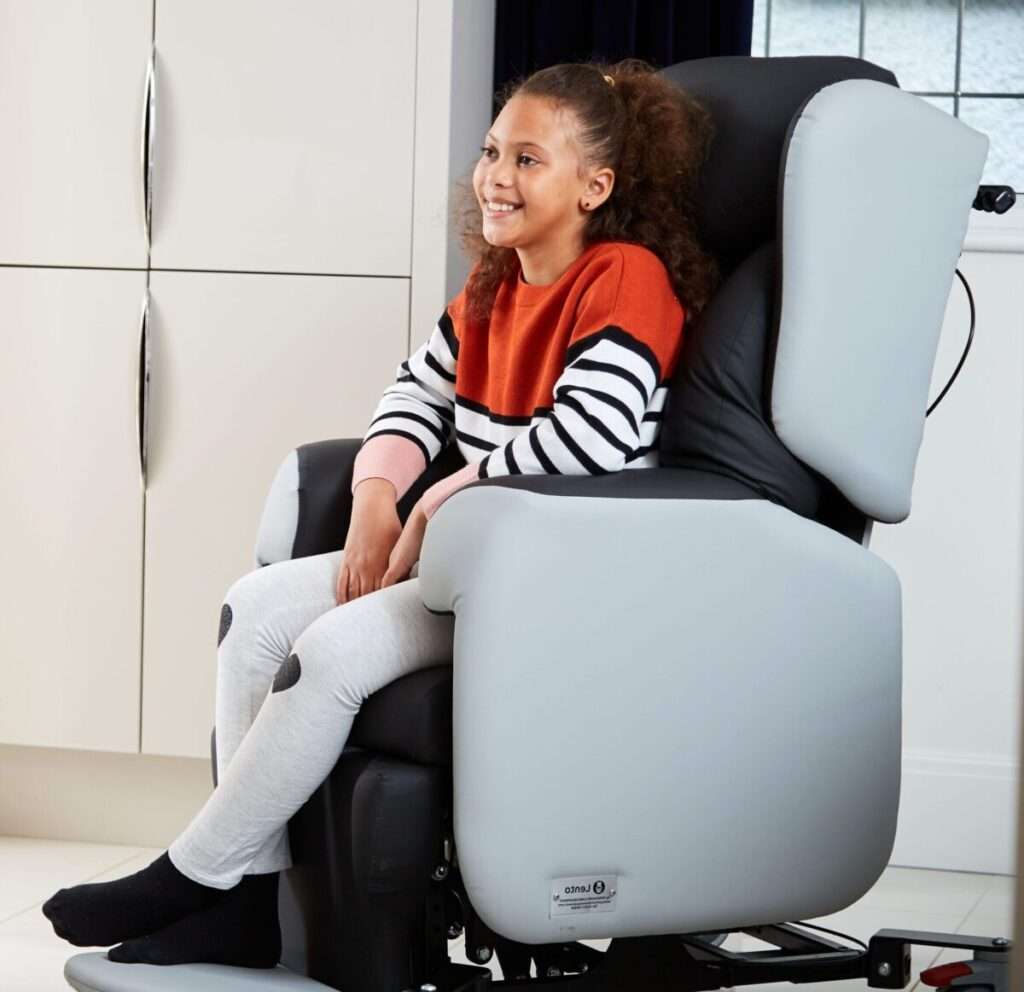
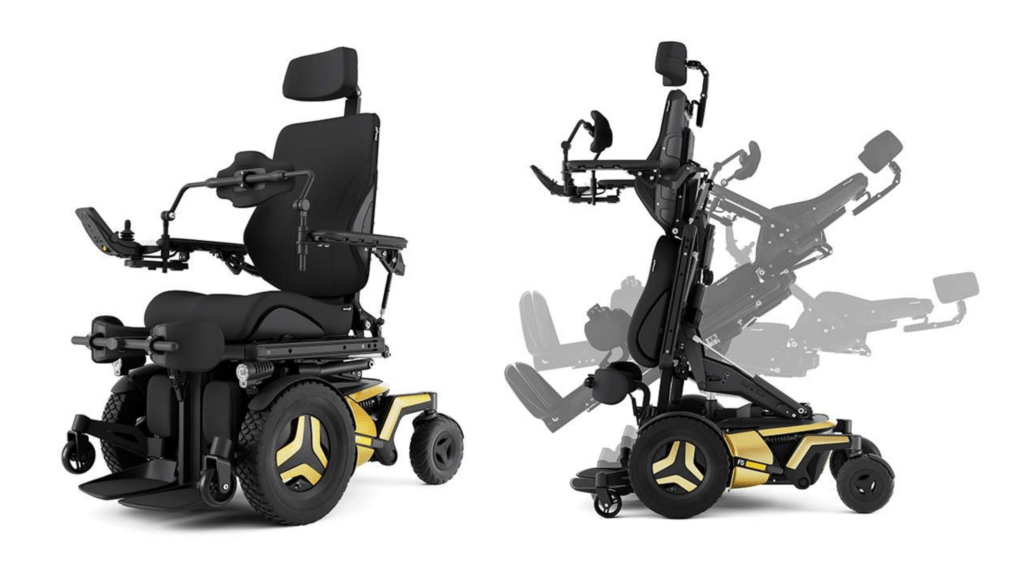
The Duo care chair and Lento are both excellent options for brain injury rehabilitation. They have a modular design which allows you to easily adjust the levels of pressure relief and postural support to provide to correct level of comfort and control for the user at any stage of their rehabilitation journey
Be prepared for the most severe cases
Whilst brain injury patients do often see improvements over time, there are also many cases where symptoms will worsen in the first few weeks after injury. There will also be patients who unfortunately don’t respond to rehabilitation as well as healthcare professionals had hoped. These patients may then be left with severe impairments, like paralysis or involuntary movement, for life.
Brain injury can be an extremely unpredictable condition. By specifying a highly flexible chair that works for even the most high-dependency users, you can make sure brain injury patients have a chair that will work for them long-term if needed.

Lento care chair with cocoon backrest
The Lento care chair is fully adjustable, so you can alter the posture support and pressure relief levels to suit patients from low risk up to high risk. You can even add a cocoon backrest that moulds around the user for patients who need high levels of trunk support. All cushions can be removed and the covers are washable for easy cleaning if the patient suffers with incontinence.
The huge number of adjustable features mean the Lento will work for around 80% of the population. This makes it an excellent chair for brain injuries to be stocked in equipment loan stores. Whichever symptoms a brain injury patient presents with, and however long-lasting they may be, the Lento is likely able to provide the support they need.
When one patient no longer needs the chair, it can be quickly cleaned, resized without tools, and used to help another patient.
Effects of Brain Injury
Once you’ve factored in the flexible features a chair needs to support someone with brain injury, it is also important to consider how the individual has been affected by their injury.
We’ve highlighted how diverse the effects of brain injury can be. So, now let’s take a look at some of the most common effects of brain injuries and how specialist seating can provide support.
Chairs for people with physical impairments
Brain injuries to the motor cortex or cerebellum will often have lasting effects on mobility. Paralysis and involuntary movement are two common physical effects of brain injury in these areas.
Paralysis
When it comes to seating for people who are paralysed due to brain injury, there are two key issues you want a chair to help combat.
- Pressure sores – People with paralysis can’t always reposition themselves unaided. This means pressure builds up in the areas that are in constant contact with the chair. Without assistance, this pressure will result in painful open wounds.Tilt-in-space is a feature to look for in a chair to help prevent pressure sores. This feature works to reposition the user throughout the day. It redistributes their body weight over a wider surface area, so pressure doesn’t build up too much in any one area.

The Lento care chair has tilt-in-space functionality built-in to help the user maintain good posture and avoid pressure sores
- Personal care – Individuals with severe paralysis will also need assistance with personal care. This includes transfers, toileting and washing. Choosing a chair that is compatible with hoists can make personal care easier for brain injury patients and their carers.

The Lento has been designed for patients that are hoisted. When the chair is in an upright position, there is plenty of space to use a mobile hoist.
If a patient isn’t hoisted but does rely on side transfers to move from their chair to a wheelchair then removable armrests is a feature to look out for. Being able to quickly take off the armrest makes it much quicker and easier to insert transfer aids and help a patient to slide across from one chair to another.
Removable armrests also allow you to provide some personal hygiene assistance whilst the patient is still seated. You can help them to get dressed without having to fully transfer them out of their chair.
Involuntary movement
Safety is the primary concern for brain injury patients with involuntary movement. They need a chair that is strong and durable that won’t be damaged and become an injury risk if the patient experiences strong tremors.

A Copgrove chair is a good option for more independent and mobile brain injury patients who need a rise and recline chair not a care chair. It provides standing support for individuals whose tremors affect their balance.
Padding is also important to protect the patient. If you choose a chair that’s hard or has sharp corners, they may injure themselves.

The Lento is fully padded for comfort and safety.
Chairs for people with cognitive impairments
Common cognitive effects of brain injuries include reduced concentration and impaired reasoning. It may not seem immediately obvious how seating can help with these issues. But there are features you can look for in a chair that help to care for someone with cognitive impairments.
Reduced concentration
People with a reduced concentration span may forget about things like maintaining good posture and changing position when they start to feel uncomfortable. So even though some brain injury patients may be physically able to sit up straight and reposition themselves they may not have the cognitive awareness to do so unaided.
Therefore, it can be helpful to choose a chair with features that support posture and positioning. Chairs with adjustable backrest recline can help to prevent the user from slipping down in the chair. If someone starts to slump forward in their chair, adjusting the back angle can open the body back up and ensure their lower back and buttocks stay correctly positioned at the back of the chair.
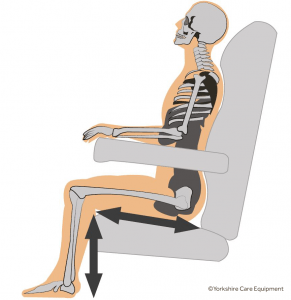
Impaired reasoning
Impaired reasoning presents a safety risk for patients using specialist seating. They may try to get up when the legrest is elevated producing a trip hazard. Or, they may attempt to get up suddenly when nobody is available to assist them, and they aren’t physically able to stand unaided.
In these circumstances, you may want to avoid chairs with patient handset controls. This will reduce the risk of them moving their chair in a way that could injure them or others.
There may even be a need to choose a chair with restraints. A lap belt is a common chair restraint. It secures the user in place and can prevent them from slipping out of the chair or from getting up when there’s a risk of injury.
We would recommend a chair where restraints can be added if needed, rather than being a permanent feature. It is important to remember that restraints should only be used if deemed necessary by a patient’s primary care team.
For more help on assessing whether restraints are appropriate for a patient, read our Seating Restraints Guide.
Chairs for people with behavioural impairments
Changes in behaviour are another common effect of brain injury. Sometimes these are as a direct result of damage to the brain e.g. personality changes and disinhibition. But often they are more indirect, some patients will become depressed and withdrawn after experiencing a life-changing brain injury.
It is important then that chairs for brain injury patients help them to socialise and communicate with others. Two key features that can support patients’ mental wellbeing are wheels and headrests.
A chair with wheels is easy to move between rooms. This helps patients who are confined to their chair to continue socialising with others. They can move from their bedroom to communal areas quickly without having to be transferred to a wheelchair.
If communication is a concern, you may also want to avoid chairs with extended headrests. A headrest that supports the sides of the head is good for patients who cannot support their own head. But it’s extended profile can obstruct the user’s view, making it harder for them to take in their surroundings and communicate with others.

You can change the head cushion on the Lento in seconds to get support/visibility as and when you need it.
Summary
Brain injury is a very complex and often unpredictable condition. Patient needs can vary greatly from one person to another. This can make it difficult to specify specialist seating for brain injury patient. In this guide, we cover the importance of choosing a chair that is flexible enough to work for a patient as their condition improves for rehabilitation purposes. We also offer recommendations for the features you should look for in a chair to support specific physical, cognitive and behavioural impairments associated with brain injury. Due to its versatility, the Lento care chair is one of our top picks for specialist seating for brain injury patients.