Falls are a significant concern for patients admitted to NHS hospitals. Inpatient falls are unintentional falling incidents that occur while someone is in hospital. They can lead to severe injuries such as fractures, traumatic brain injury, fatal injury, decreased quality of life, and increased healthcare costs.
Injuries resulting from inpatient falls increase a patient’s length of stay in hospital and may result in the need for further medical interventions.
There are ongoing efforts to prevent and reduce the number of falls that occur. By implementing best practices and evidence-based interventions, hospitals can help ensure the safety and well-being of their patients.
Inpatient Falls can lead to:
- Severe injuries that can prolong hospital stays.
- Result in legal action against the hospital.
- Increased healthcare costs
The Importance of Preventing Inpatient Falls in Hospitals
In 2011, inpatient falls accounted for 324,000 (26%) of all patient safety incidents in hospitals. Many of these costs attributed to increased length of stay and rehabilitation costs. Inpatient falls disproportionately affect older patients due to factors ranging from reduced mobility, side effects from multiple medications, and underlying health conditions.
The Royal College of Physicians (RCP) estimated that in the same period, fragility fractures, commonly associated with falls in older people, were estimated to cost the NHS more than £2 billion a year.
Another RCP report estimated that the costs of inpatient falls in a typical acute hospital range between £80k to £500k annually, the same report also notes that “improving inpatient falls prevention reduces length of stay and, therefore, cost while improving quality”.
Inpatient falls are a significant concern for healthcare providers. Outside of the adverse physical and financial outcomes of falls, inpatient falls can also lead to a loss of confidence in the hospital by patients and their families. All these reasons mean that healthcare providers must work to prevent falls to ensure the safety of their patients and help maintain business sustainability.
How Often Do Inpatients Fall in Hospitals?
In the UK, falls are the most reported patient safety incident in hospitals. NHS England reported that around 240,000 falls occur in hospitals in England and Wales each year, with roughly one in three patients aged 65 or over falling at least once during their hospital stay.
The National Audit of Inpatient Falls Commissioners’ report (2015) identified that:
- The average number of falls per 1,000 Occupied Bed Days is 6.63.
- The average number of falls resulting in moderate harm, severe harm, and fatality per 1,000 OBDs is 0.19
This means that for every 1,000 days a patient spends in a hospital bed, there were 6.63 reported falls and 0.19 resulted in injury.
*These rates were measured across most trusts and local health boards (LHBs) in England and Wales.
The frequency of inpatient falls in UK hospitals varies depending on several factors, such as patient age, medical conditions, medications, and the type of healthcare facility.
What Equipment do Hospitals Use Lift Fallen Patients?
In UK hospitals, there are a range of lifting equipment options available to help safely move and lift inpatients who have fallen. The type of patient lifting equipment used will depend on the patient’s individual needs and the hospital’s policies and procedures.
Safe moving and handling equipment for patient lifts can allow a carer or nurse to aid patients with a variety of daily actions in a reliable and dignified way. Some examples of the types of patient lifting equipment commonly used in UK hospitals include:
Mobile Hoists
Mobile hoists come in different designs, but they typically consist of a wheeled base, a vertical mast, and a lifting mechanism. The lifting mechanism may be manual or electric, and it usually consists of a sling or harness that is attached to the hoist’s lifting arm.
To use a mobile hoist, the individual to be lifted is first placed into the sling or harness. The hoist is then positioned over the individual, and the lifting arm is lowered to secure the sling or harness to the hoist. Once the individual is securely attached to the hoist, the lifting mechanism is activated, and the hoist raises the individual off the ground. The hoist can then be moved to another location, and the individual can be lowered and released from the sling or harness.
Mobile hoists are designed to be easy to manoeuvre, with features such as adjustable leg widths and height-adjustable masts to accommodate different lifting situations.
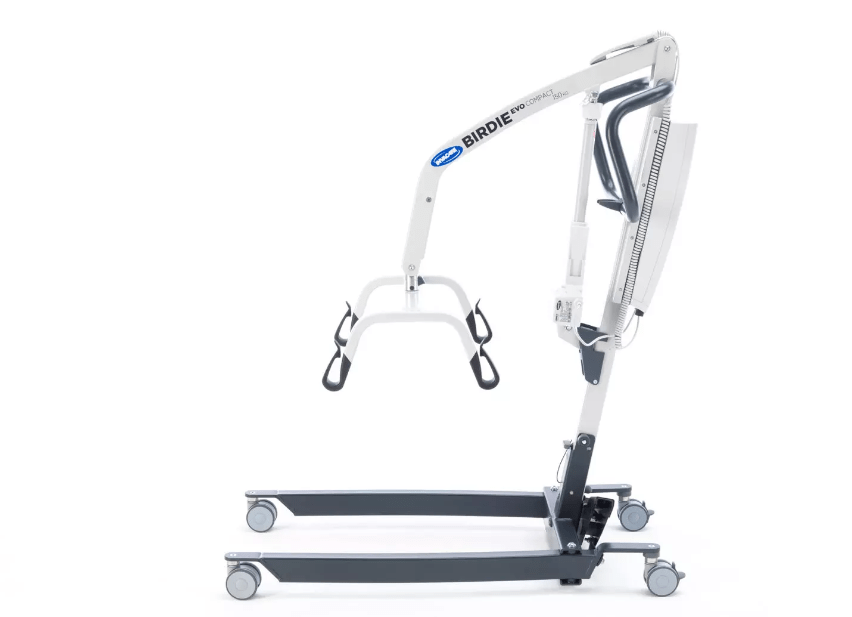

Mobile hoists are designed to be safe and stable, with locking mechanisms to prevent the hoist from tipping over during use.
Sling Selection:
Choosing the right sling is essential for patient comfort and safety when using a mobile hoist. There are different types of slings available, and the type of sling you choose will depend on the individual’s needs and abilities. From full-body slings, leg slings, and standing slings. The choice of sling will depend on the patient’s needs and mobility.
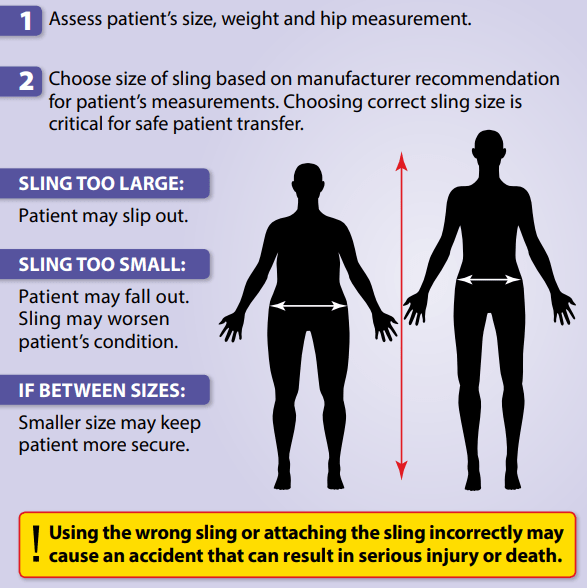
Sling selection is hugely important when using a mobile hoist to perform a full body lift of a patient. Getting this correct is essential.
- Consider the individual’s needs: The first thing to consider is the individual’s physical abilities and any medical conditions they may have. For example, if the individual has limited upper body strength or mobility, you may need to use a full-body sling that provides support for their entire body. If the individual has a skin condition or is prone to pressure sores, you may need to choose a sling with a breathable material that reduces the risk of skin irritation.
- Check the weight limit: Every sling has a weight limit, so it’s important to make sure the sling you choose can support the individual’s weight. The weight limit should be clearly labelled on the sling.
- Choose the right size: The sling should fit the individual snugly and comfortably. If the sling is too loose, the individual may slip out, while if it’s too tight, it may cause discomfort or even injury. Be sure to measure the individual carefully and choose a sling that is the right size for their body.
- Check the attachment points: The sling should be compatible with the attachment points on your mobile hoist. Some slings are designed to be used with specific types of hoists, so be sure to check the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Follow the manufacturer’s instructions: The manufacturer’s instructions will provide specific guidelines on how to use the sling safely and effectively.
Flat Patient Lift Systems
The use of a flat patient lift can make it easier and safer to move and transfer patients who have limited mobility in a hospital setting. They are essential tools for healthcare providers who need to move and transfer patients with limited mobility. These lifts can also help reduce the risk of injury to both the patient and caregiver during transfers, which is why they are regularly seen across hospitals, nursing homes, and other medical facilities.
Lifting and transferring patients manually can be challenging and put caregivers at risk for injury. Flat patient lifts provide a safer and more controlled method of transfer, reducing the risk of injury to both the patient and the caregiver. This kind of patient lift can also improve comfort comfort and and raise a patient in a dignified way by providing a more controlled and gentle transfer process.
Inflatable Patient Lifts
Inflatable patient lifts are a relatively new type of lifting equipment used in hospitals to transfer patients from one surface to another. Unlike traditional lifts, which use mechanical or hydraulic systems to lift and transfer patients, inflatable lifts use air pressure to lift and support the patient.
Inflatable patient lifts typically consist of a soft, inflatable cushion that is placed under the patient, along with an air compressor or pump that inflates the cushion. Once inflated, the cushion provides a stable and supportive surface on which the patient can be lifted and moved to another surface.
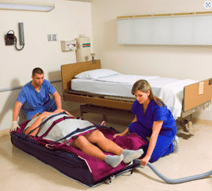
Flat patient lift system such as the Hoverjac can be inflated to lift a fallen patient.
One of the main benefits of inflatable patient lifts is their portability and ease of use. They are lightweight and can be easily transported to different areas of the hospital, making them ideal for use in emergency situations or for patients who require frequent transfers. In addition, they are designed to be easy to use, even by healthcare professionals who have little experience with lifting equipment.
Another advantage of inflatable patient lifts is that they can be used to lift patients who are in awkward or uncomfortable positions, such as those who have fallen and are lying on their side or stomach. The soft, flexible cushion can conform to the patient’s body, providing support and stability during the transfer.
Inflatable patient lifts are a useful and innovative tool for transferring patients in a hospital setting. Healthcare professionals who work with lifting equipment should be trained on the proper use of inflatable patient lifts, as well as the specific needs and considerations of each patient to ensure their safety and comfort during transfer.
Raizer Lifting Chairs
The Raizer lifting chair can be an effective solution for tackling non-injurious inpatient falls in hospitals. The device is designed to help patients who have fallen to get back on their feet quickly and safely, without the need for physical lifting or moving. By using the Raizer chair, healthcare professionals can reduce the risk of injury to both the patient and the staff, while also promoting patient independence and confidence.
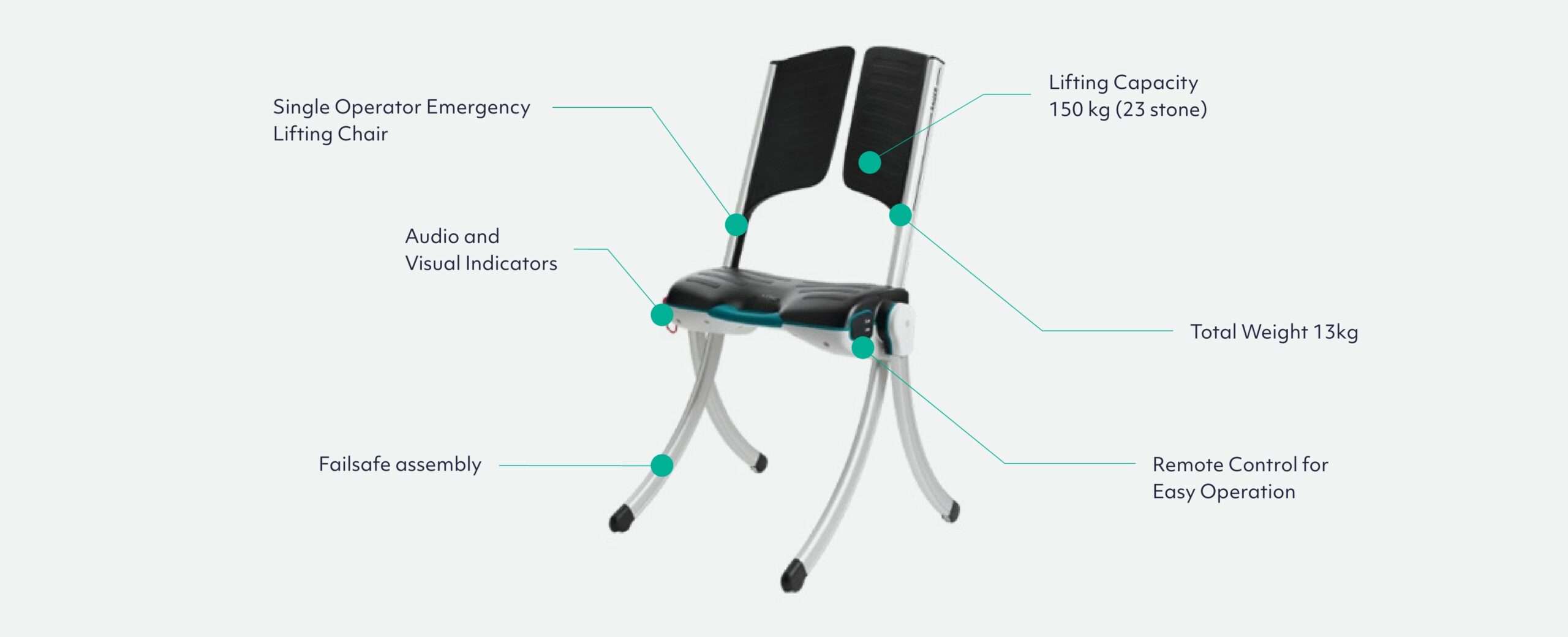
This portable and battery-operated device is often used by healthcare professionals and caregivers to reduce the risk of injury to both the person who has fallen and the person providing assistance. It can also help to restore the person’s confidence and independence, as it allows them to get up from the floor without the need for assistance from others.
You can typically find Raizer M or Raizer 2 lifting chairs patient lift device in care homes, hospitals, with emergency services, and in private homes, help people with limited mobility get up from the floor without the need for physical lifting or moving.

How the Raizer can be used to tackle non-injurious inpatient falls in hospitals:
- Reduced risk of injury: The Raizer chair can help to reduce the risk of injury to both the patient and the staff during the lifting process. This is especially important for patients who are frail or have mobility issues, as they may be at higher risk of falls and injuries.
- Improved patient outcomes: By using the Raizer chair, healthcare professionals can help patients get back on their feet quickly and safely, which can lead to improved patient outcomes, reduced hospital stays, and lower healthcare costs.
- Enhanced patient independence: The Raizer chair can help to restore the patient’s confidence and independence by allowing them to get up from the floor without the need for assistance from others.
- Easy to use and transport: The Raizer chair is easy to use and transport, making it a convenient tool for healthcare professionals to have on hand in case of falls.
- Cost-effective: Compared to other lifting devices, the Raizer chair is a cost-effective solution that can provide significant benefits to patients and healthcare facilities.
Summary
When inpatients fall in hospitals, lifting equipment is used to ensure that they are lifted safely and effectively without causing any further harm. The type of lifting equipment used will depend on the specific needs of the patient, their medical condition, and the extent of their injuries.
Some of the most commonly used lifting equipment in hospitals include floor lifts, sit-to-stand lifts, ceiling lifts, and transfer boards. Each of these devices has its unique features and benefits, which make them suitable for different types of patients and situations.
Flat floor lifts, for instance, are ideal for lifting patients from the floor or low surfaces, while sit-to-stand lifts are used to help patients who have difficulty standing up from a seated position. Tackling non-injurious inpatient falls, on the other hand, may require a different lifting device to provide the most effective solution.
Regardless of the type of lifting equipment used, it is essential that healthcare professionals are trained to use it correctly to avoid accidents and injuries. Adequate training and education can also help to ensure that patients receive the best possible care and treatment when they fall.
Using appropriate lifting equipment can help healthcare professionals ensure that patients are lifted safely and effectively, while also promoting patient independence, confidence, and well-being.